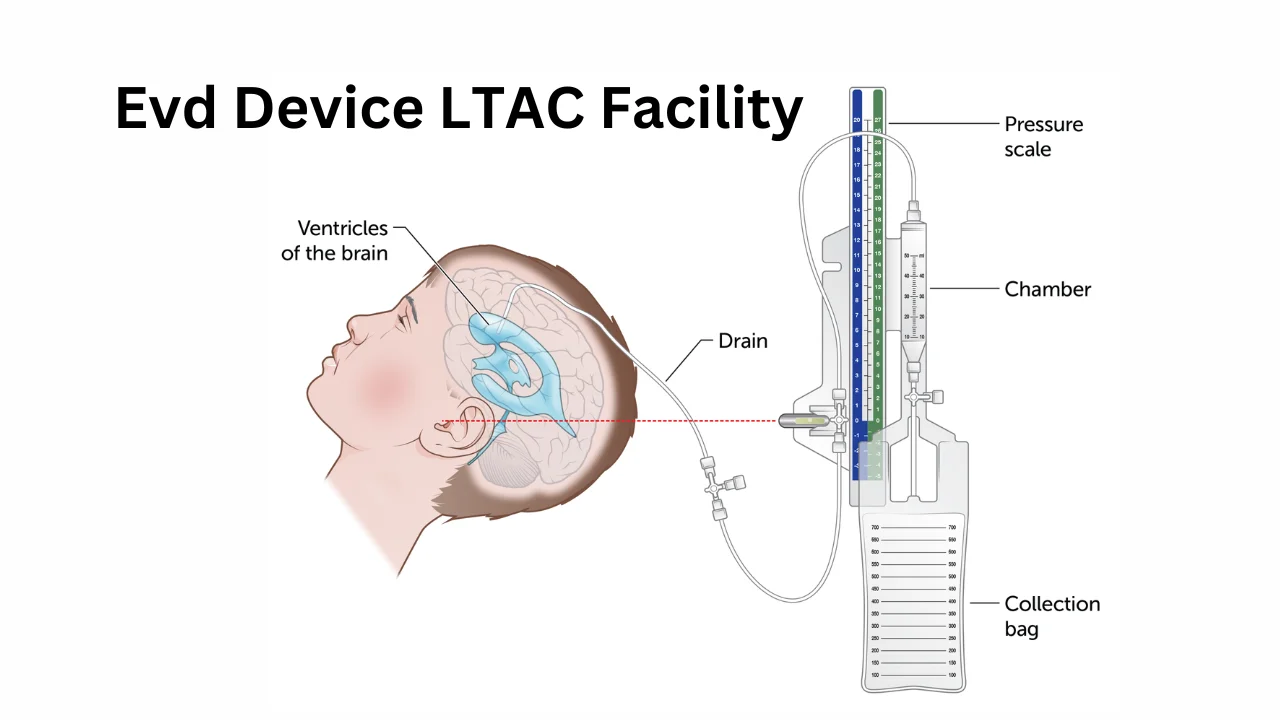
LTAC facilities use the EVD device, a crucial medical tool, to manage critically ill patients with neurological conditions. This device, known as an external ventricular drain, monitors and relieves pressure inside the brain caused by excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Long-term acute care facilities specialize in providing extended care for patients with complex medical needs, including those who require neurological monitoring.
What Is an EVD Device?
An external ventricular drain (EVD) is a temporary device used to drain excess CSF from the ventricles of the brain. CSF buildup can occur due to trauma, infection, or other neurological conditions. The device also measures intracranial pressure, which helps medical teams monitor and respond to changes in the patient’s condition. Proper handling of an EVD device in an LTAC facility is vital for improving patient outcomes.
ALSO READ: kodi Addons Fentastic How To Make Widget Text Bold
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Drains excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and monitors intracranial pressure. |
| Common Conditions | Hydrocephalus, traumatic brain injuries, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and meningitis. |
| Key Components | Catheter, drainage system, pressure monitoring unit, adjustable valves. |
| Benefits in LTAC | Precise pressure monitoring, effective fluid management, and improved patient outcomes. |
| Risks | Infection, device malfunction, and patient discomfort. |
| Maintenance | Regular monitoring, hygiene protocols, and adjustments by trained medical professionals. |
| Innovations | Antimicrobial catheters, digital monitoring systems, and enhanced drainage controls. |
| Duration of Use | Typically temporary, ranging from a few days to weeks, based on medical needs. |
Why Are EVD Devices Necessary in LTAC Facilities?
LTAC facilities cater to patients with severe and chronic medical conditions, including those recovering from brain injuries or surgeries. For patients with conditions like hydrocephalus, traumatic brain injuries, or infections causing CSF accumulation, the EVD device serves as a lifeline. Its ability to relieve pressure helps prevent brain damage and supports recovery during the patient’s stay in the facility.
ALSO READ: H Montanaro Teacher Cranston Eden Park Inspires Young Minds
How Does an EVD Device Work?
An EVD device works by inserting a catheter into the brain’s ventricles to allow excess CSF to drain. The catheter is connected to an external system that collects the fluid and measures its pressure. In LTAC facilities, trained professionals monitor the drainage system, adjust the settings, and ensure it functions effectively to meet patient needs.
Key Benefits of EVD Devices in LTAC Facilities
The integration of an EVD device in an LTAC facility offers several benefits:
Precise Pressure Monitoring:
These devices provide real-time data on intracranial pressure.
Effective Fluid Management:
They prevent complications related to CSF buildup.
Improved Patient Outcomes:
By reducing pressure, they lower the risk of permanent brain damage.
EVD devices are indispensable in providing specialized care in LTAC settings, ensuring patients receive appropriate neurological support.
Common Conditions Treated With EVD Devices in LTAC Facilities
Several medical conditions necessitate the use of EVD devices in LTAC facilities. These include:
Hydrocephalus:
A condition where excess CSF accumulates in the brain.
Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI):
Often caused by accidents or falls, leading to pressure buildup.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage:
Bleeding in the brain that can increase CSF levels.
Infections like Meningitis:
Can lead to blocked fluid pathways, requiring drainage.
Components of an EVD Device
An EVD device comprises several critical components that work together to manage CSF levels. These include:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Catheter | Inserted into the brain to drain CSF. |
| Drainage System | Collects and measures the drained fluid. |
| Pressure Monitoring Unit | Tracks intracranial pressure in real time. |
| Adjustable Valves | Controls the rate of fluid drainage to prevent complications. |
The maintenance of these components is vital to ensure accurate performance in an LTAC facility.
The Role of Healthcare Teams in Managing EVD Devices
Managing an EVD device in an LTAC facility requires a multidisciplinary team. Doctors, nurses, and technicians work together to:
Regularly check the drainage levels.
Adjust the device settings based on patient needs.
Prevent infections by maintaining strict hygiene protocols.
Effective teamwork ensures that the device operates safely and patients receive optimal care.
Challenges in Using Evd Device LTAC Facility

While EVD devices are highly effective, their use in LTAC facilities comes with challenges:
Infection Risks:
Since the catheter creates an open pathway to the brain, infection risks are high.
Device Malfunctions:
Mechanical issues can lead to improper drainage or pressure monitoring.
Patient Discomfort:
The insertion and presence of the device can cause discomfort.
Addressing these challenges requires expertise, vigilance, and advanced medical protocols in LTAC facilities.
Innovations in EVD Devices and Their Impact on LTAC Facilities
Recent advancements in EVD devices have improved their effectiveness in LTAC facilities. Innovations like antimicrobial catheters and digital monitoring systems have reduced infection rates and enhanced accuracy. These improvements have made EVD devices safer and more reliable, benefiting patients who need long-term neurological care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an EVD device used for in an LTAC facility?
An EVD device in an LTAC facility is used to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the brain and monitor intracranial pressure.
How long can an EVD device remain in place?
An EVD device is typically used for a short term, ranging from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the patient’s condition.
Are there risks associated with using an EVD device?
Yes, risks include infection, device malfunction, and bleeding, but these are minimized with proper care in LTAC facilities.
Conclusion
The integration of an EVD device in an LTAC facility plays a critical role in managing patients with severe neurological conditions. By monitoring and controlling intracranial pressure, these devices prevent complications and support recovery. With continued advancements and skilled medical teams, EVD devices will remain a cornerstone of specialized care in LTAC facilities.